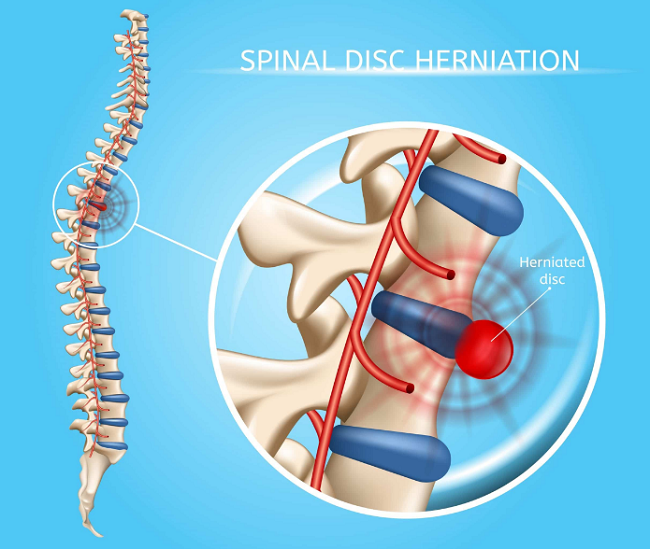
Surgery is sometimes necessary to treat a herniated disc that has not responded to conservative treatment options. Discectomy, a common surgical procedure for herniated discs, involves the removal of the damaged portion of the disc to alleviate pressure on the nerves. This article will discuss various surgical options for herniated discs, the risks involved, and factors to consider when deciding on surgery.
Discectomy for Herniated Disc
Discectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the herniated portion of an intervertebral disc. The goal is to alleviate pressure on the nerves, thereby relieving pain and other symptoms. Discectomy can be performed through various techniques, such as microdiscectomy (a minimally invasive approach) or open discectomy (a more traditional surgery). The choice of technique depends on the specific circumstances and the surgeon’s expertise.
Other Herniated Disc Surgery Options
Aside from discectomy, other surgical options for treating herniated discs include:
- Laminectomy: Removal of the lamina, the bony part of the vertebrae, to create more space for the nerves and reduce pressure on the spinal cord.
- Artificial Disc Replacement: Replacement of the damaged disc with an artificial one, maintaining the natural function and movement of the spine.
- Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more adjacent vertebrae together to provide stability and eliminate motion at the affected spinal segment.
Risks of Herniated Disc Surgery
As with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with herniated disc surgery. Some common risks include:
- Infection
- Excessive bleeding
- Nerve damage
- Anesthesia complications
- Recurrent herniation
- Failure to alleviate symptoms
It is essential to discuss these risks with your surgeon and weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of surgery.
Neurosurgeon for Herniated Disc
A neurosurgeon is a medical specialist who is trained to perform surgeries on the nervous system, including the brain and spine. When considering surgery for a herniated disc, it is important to consult with a neurosurgeon experienced in treating spinal disorders to ensure the best possible outcome.
Herniated Thoracic Disc Surgery
Surgery for herniated thoracic discs is relatively rare compared to cervical and lumbar disc surgeries, as thoracic disc herniations occur less frequently. However, when necessary, surgical options may include discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion, depending on the specific circumstances and severity of the herniation.
L4-L5 and L5-S1 Herniated Disc Surgery
L4-L5 and L5-S1 are common locations for lumbar disc herniation. Surgical options for these levels include discectomy, laminectomy, artificial disc replacement, or spinal fusion. The choice of surgery depends on the severity of the herniation, the presence of spinal instability, and the surgeon’s recommendations.
Conclusion
Surgery for herniated discs, such as discectomy, can provide significant relief for patients who have not responded to conservative treatment options. It is crucial to consult with an experienced neurosurgeon to discuss the risks and benefits of surgery and determine the most appropriate course of action. By carefully considering all factors and working closely with healthcare professionals, patients can make informed decisions about their spinal health and achieve the best possible outcomes.