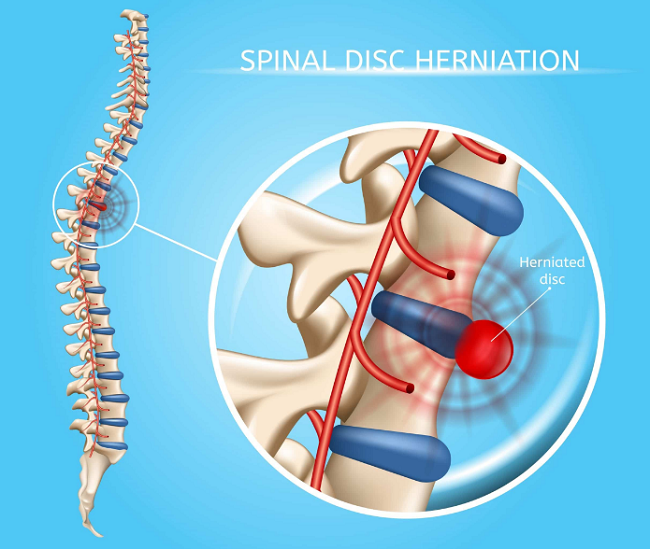
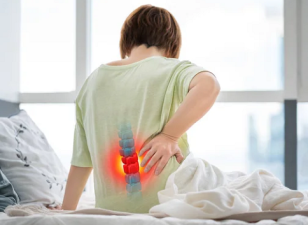
Herniated discs, also known as slipped or ruptured discs, can cause a wide range of symptoms, from localized pain to radiating discomfort and numbness in the extremities. Recognizing the signs of a herniated disc is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and addressing the underlying issue. This article will discuss the symptoms, complications, and differential diagnosis of herniated discs, helping individuals recognize the condition and seek proper medical care.
Signs of a Herniated Disc
Common signs of a herniated disc include:
- Localized pain in the affected area of the spine
- Radiating pain, numbness, or weakness in the extremities
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Muscle spasms
- Muscle atrophy (in severe cases)
Foot Drop Due to Herniated Disc
Foot drop, a condition in which an individual has difficulty lifting the front part of the foot, can be a sign of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine. This occurs when the herniated disc compresses the nerve responsible for controlling the muscles involved in foot movement. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are necessary to prevent permanent nerve damage and improve function.
Leg Pain and Numbness from Herniated Disc
A herniated disc in the lumbar spine can cause leg pain and numbness. This occurs when the herniated disc compresses a nerve that serves the leg, leading to radiating pain or numbness along the path of the affected nerve.
Herniated Disc Numbness in Toes
A herniated disc can cause numbness in the toes if the compressed nerve serves the area of the foot. This numbness can be an important symptom to discuss with a healthcare professional, as it may help pinpoint the location of the herniation and inform appropriate treatment.
Herniated Disc vs. Muscle Strain
A herniated disc can sometimes be mistaken for a muscle strain, as both conditions can cause localized pain and discomfort in the back. However, a herniated disc typically presents with additional symptoms, such as radiating pain, numbness, or weakness in the extremities. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause of back pain and guide appropriate treatment.
Muscle Atrophy and Spasms from Herniated Disc
A herniated disc can cause muscle atrophy, or the loss of muscle mass, in severe cases where nerve compression leads to prolonged weakness and disuse of the affected muscles. Additionally, herniated discs can cause muscle spasms as the body attempts to stabilize the affected area and protect it from further injury.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of a herniated disc is essential for seeking appropriate treatment and addressing the underlying cause of back pain and discomfort. Symptoms such as radiating pain, numbness, and muscle spasms can help differentiate a herniated disc from other potential causes of back pain, such as muscle strains. If you suspect you have a herniated disc, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action and develop a tailored treatment plan to promote recovery and improve spinal health.