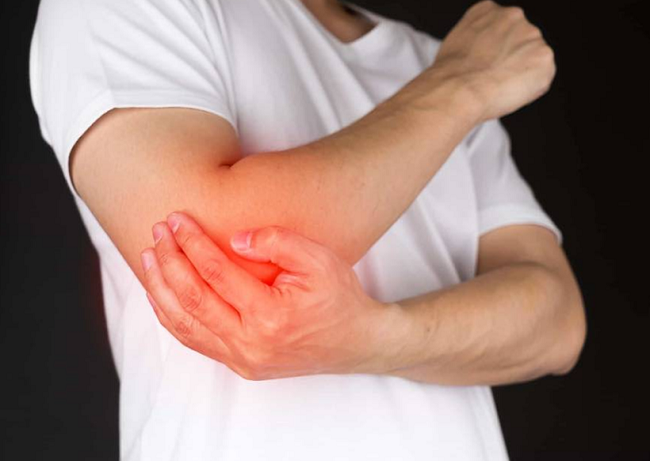
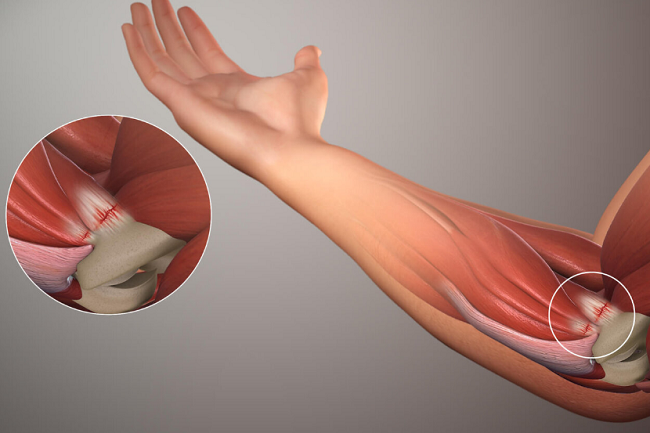
Golfer’s elbow is a condition that affects the tendons and muscles that attach to the medial epicondyle, which is the bony bump on the inside of the elbow. These tendons and muscles are responsible for flexing the wrist and fingers, which are essential movements in golf swings and other sports activities.
The condition usually occurs due to overuse or repetitive strain injury, causing micro-tears in the tendons and muscles of the forearm. This injury leads to inflammation and pain in the elbow, which can affect daily activities, including sports performance.
Anatomy of the Elbow
To understand golfer’s elbow, it is essential to understand the anatomy of the elbow joint. The elbow is a hinge joint that connects the upper arm bone (humerus) and two forearm bones (radius and ulna). The bony bump on the inside of the elbow is called the medial epicondyle, which serves as an attachment site for the muscles and tendons that move the wrist, hand, and fingers.
Causes of Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s elbow is primarily caused by overuse or repetitive strain injury, leading to micro-tears in the tendons and muscles that attach to the medial epicondyle. Some common activities that can lead to golfer’s elbow include:
- Golf swings
- Throwing sports
- Weightlifting
- Repetitive gripping
- Carrying heavy objects
- Repetitive computer use
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing golfer’s elbow, including:
- Age (most common in people between 40 and 60)
- Previous elbow injury
- Poor technique in sports activities
- Overuse or repetitive strain injury
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow
- The most common symptoms of golfer’s elbow include:
- Pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow
- Stiffness and weakness in the forearm
- Difficulty in gripping or lifting objects
- Numbness or tingling sensation in the fingers
- Pain worsening with certain activities, such as golf swings or gripping objects
Diagnosis
To diagnose golfer’s elbow, a doctor will perform a physical examination of the elbow and ask about the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Additional tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be needed to rule out other conditions or assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options
Treatment for golfer’s elbow depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s symptoms. Surgical and Non-surgical treatment.
Surgical Treatment
If non – surgical treatments do not provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for golfer’s elbow may include:
- Arthroscopic surgery: A minimally invasive procedure in which a small camera and surgical instruments are inserted through small incisions in the elbow to repair or remove damaged tissue.
- Open surgery: A more invasive procedure in which a larger incision is made in the elbow to repair or remove damaged tissue.
Non – surgical Treatment
Non – surgical treatment options for golfer’s elbow may include:
- Rest: Avoiding the activities that caused the injury and giving the elbow time to heal can help relieve pain and prevent further damage.
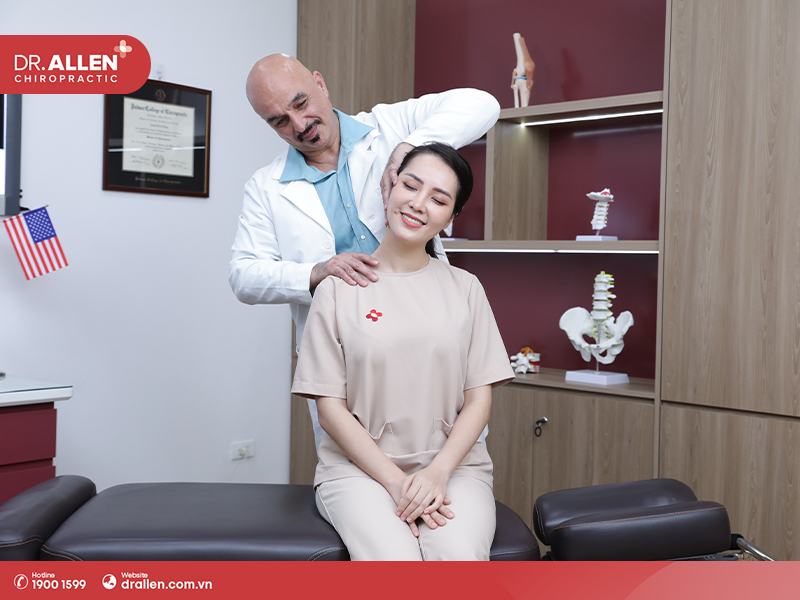
- Chiropractic care for golfer’s elbow may involve a combination of soft tissue therapy, joint manipulation, and rehabilitation exercises.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Compression: Wearing a compression bandage or brace around the elbow can help reduce swelling and provide support to the affected area. - Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can help patients learn exercises to strengthen the muscles and tendons in the forearm and elbow, improving flexibility and reducing pain.
- Medications: Over – the – counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Prevention
To prevent golfer’s elbow, individuals should:
- Warm up before sports activities and stretch regularly.
- Use proper technique and form during sports activities.
- Avoid overuse or repetitive strain injuries by taking breaks and resting.
- Strengthen the muscles and tendons in the forearm and elbow through regular exercise and physical therapy.
Recovery Time
The recovery time for golfer’s elbow varies depending on the severity of the injury and the type of treatment. Mild cases may only require a few weeks of rest and physical therapy, while more severe cases may require several months of treatment and recovery.
Complications
Complications from golfer’s elbow are rare but may include:
- Chronic pain or stiffness in the elbow.
- Reduced range of motion in the elbow.
- Recurring or persistent symptoms despite treatment.
If you’re struggling with golf elbow, you know how frustrating and painful it can be. While there are many treatment options available, chiropractic care can be a highly effective choice. Chiropractors are experts in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions, including golf elbow. They use a variety of techniques to reduce pain and inflammation, improve joint mobility, and promote healing. Chiropractic care is non – invasive and drug – free, making it a safe and natural option for those looking to relieve their golf elbow symptoms. By addressing the root cause of your golf elbow, chiropractic care can provide long – term relief and help you get back to enjoying your favorite activities pain – free.