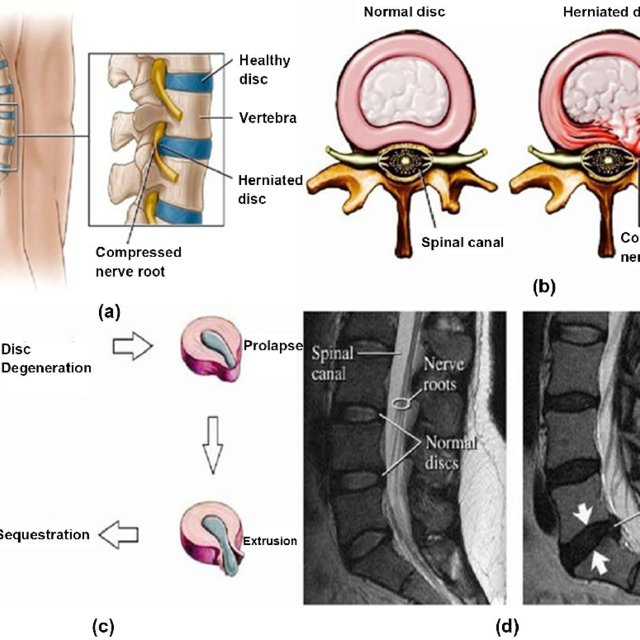
Herniated discs can occur at various levels of the lumbar spine, from L1 to S1. The lumbar region consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5) that support the upper body and facilitate movement, and the sacrum (S1) at the base of the spine. In this article, we will discuss the differences and similarities between herniated discs at different lumbar levels, focusing on L1-S1, and explore their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Herniated Disc at L4-L5
The L4-L5 disc is located between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae and is one of the most common sites for disc herniation. A herniated disc at this level can lead to symptoms such as:
- Lower back pain
- Sciatica, or pain radiating down the buttocks, thigh, and leg
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the leg or foot
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods
Herniated Disc at L3-L4
A herniated disc at the L3-L4 level is less common than at L4-L5 but can still cause significant discomfort and disability. Symptoms of an L3-L4 herniated disc may include:
- Lower back pain
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the front of the thigh
- Weakness in the quadriceps (front thigh muscles)
- Difficulty climbing stairs or lifting objects
L1-S1 Herniated Disc
The term “L1-S1 herniated disc” is often used to refer to a herniated disc that occurs somewhere within the lumbar spine region, from the first lumbar vertebra (L1) to the sacrum (S1). Symptoms of an L1-S1 herniated disc can vary depending on the specific level of the herniation, but they generally involve lower back pain and neurological symptoms in the lower extremities.
S5-L1 Herniated Disc
The S5-L1 herniated disc is an alternative way of referring to an L5-S1 herniated disc, which is located between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the sacrum. This level is another common site for disc herniation and can cause symptoms such as:
- Lower back pain
- Sciatica, or pain radiating down the buttocks, leg, and into the foot
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the leg or foot
- Difficulty walking, standing, or sitting for extended periods
Treatment Options for Lumbar Herniated Discs
Treatment for lumbar herniated discs, regardless of their specific level, typically begins with conservative measures, including:
- Rest and activity modification
- Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy to strengthen core and back muscles
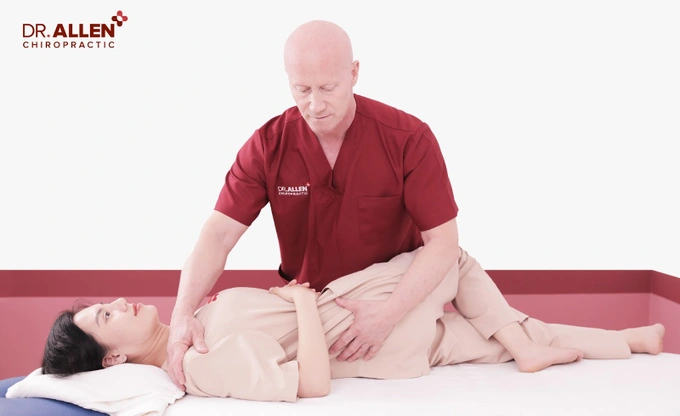
- Chiropractic care or spinal manipulation
If conservative treatments are unsuccessful or neurological symptoms worsen, more invasive options may be considered, such as epidural steroid injections or surgery.
Conclusion
Herniated discs at various levels of the lumbar spine can cause a range of symptoms and complications. Identifying the specific level of the herniation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention, including conservative measures like medication, rest, and physical therapy, can help manage symptoms and promote healing. In more severe cases, invasive interventions may be necessary to alleviate pain and restore function. By working closely with healthcare professionals and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals with lumbar herniated discs can work towards long-term recovery and improved spinal health.