A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a condition that affects the spine. It occurs when the soft, gel-like substance inside a spinal disc pushes through the tough outer layer. This can result in pain, numbness, or weakness in various areas of the body. In this article, we will explore what causes herniated discs, the differences between an annular tear and a herniated disc, symptoms, and various treatment options available.
Herniated Disc: Definition and Causes
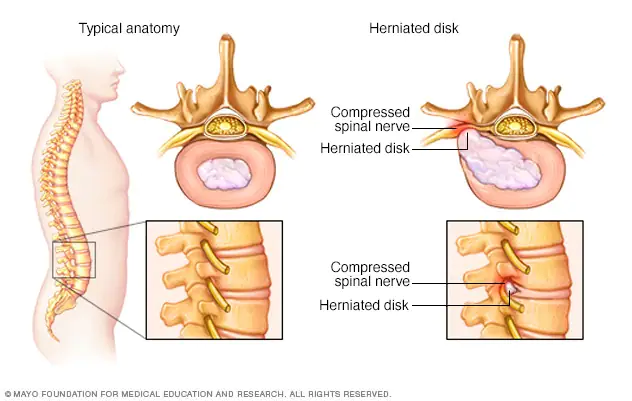
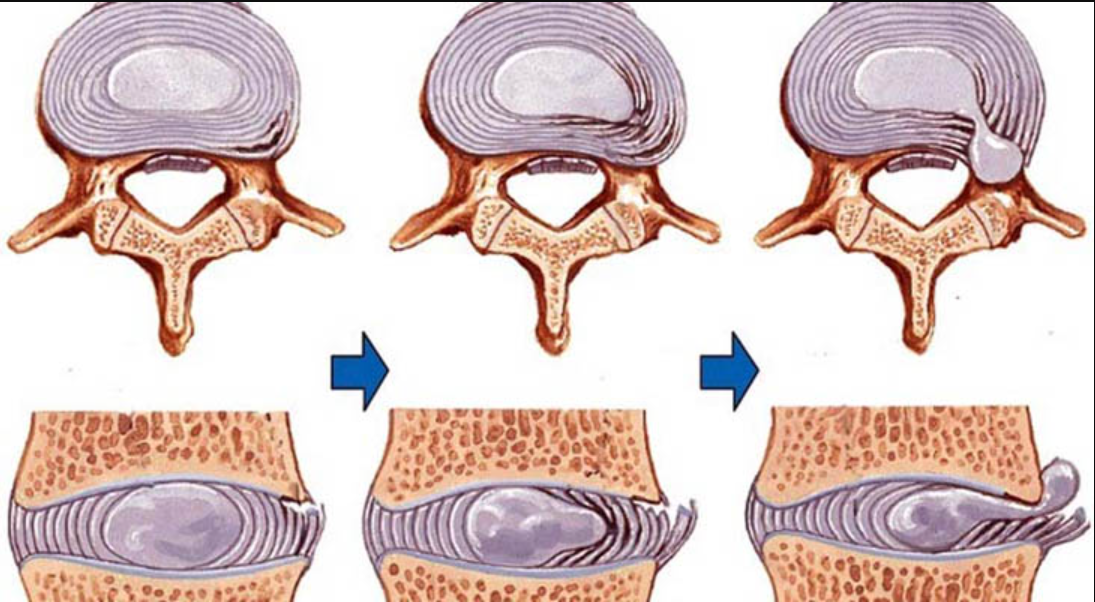
A herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus, the soft inner core of an intervertebral disc, pushes through the annulus fibrosus, the tough outer layer. This can cause irritation or compression of nearby spinal nerves, leading to various symptoms. Common causes of herniated discs include aging, trauma, poor posture, and repetitive strain.
Annular Tear vs. Herniated Disc
An annular tear is a small tear in the annulus fibrosus, which may or may not lead to a herniated disc. While both conditions can cause pain and discomfort, a herniated disc is typically more severe due to the potential for nerve compression.
Notable Cases: Ben Simmons and Others
In the world of sports, herniated discs have been known to impact athletes like NBA player Ben Simmons. Despite the challenges, many individuals can still recover and resume their careers with proper treatment and rehabilitation.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
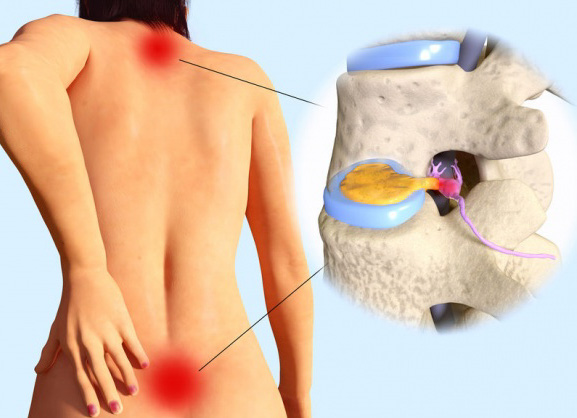
The symptoms of a herniated disc vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include localized pain, radiating pain, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and loss of reflexes. Specific symptoms can be associated with certain spinal levels, such as C4-C5, C5-C6, C6-C7, L5-S1, and S1-S2.
Herniated Disc: Emergency Symptoms
Although most cases of herniated discs can be managed conservatively, certain emergency symptoms require immediate medical attention. These symptoms include:
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: Severe lower back pain, loss of bowel or bladder control, and numbness or weakness in both legs could indicate this rare but serious condition.
- Progressive neurological symptoms: Worsening muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling in the limbs may signify nerve damage.
- Severe, unrelenting pain: If pain becomes unbearable despite medication and rest, seek medical help.
Herniated Disc: 10 Years Later
In most cases, patients experience significant improvement within a few months of conservative treatment. After 10 years, many individuals can return to normal activities, although some may continue to experience mild symptoms or occasional flare-ups. Long-term success depends on factors such as the severity of the herniation, treatment effectiveness, and adherence to a rehabilitation program.
Herniated Disc Disease
Herniated disc disease is a term used to describe a chronic condition involving one or more herniated discs. This condition can cause recurring pain, inflammation, and nerve compression. Treatment typically involves a combination of pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Herniated Disc in Vietnamese
In Vietnamese, a herniated disc is referred to as “đĩa đệm thoát vị” or “đĩa đệm bị tuột ra ngoài.” Treatment options and recommendations are similar across cultures, focusing on conservative measures and progressing to more invasive procedures if necessary.
How a Herniated Disc is Treated and Osteopathic Treatment
Initial treatment for a herniated disc often involves conservative approaches, such as medication for pain and inflammation, rest, and physical therapy. If these methods are unsuccessful, other options may be considered, including chiropractic care, osteopathic treatment, or surgery.
Osteopathic treatment for a herniated disc involves the use of manual therapy techniques, such as spinal manipulation, muscle energy techniques, and myofascial release. The goal is to reduce pain, improve mobility, and support the body’s natural healing processes.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a herniated disc typically begins with conservative measures, including rest, pain medication, and physical therapy. Other options include epidural steroid injections, chiropractic care, and osteopathic treatment. In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgery may be recommended.
Chiropractic Care and Herniated Discs
Chiropractors can provide relief for some patients with herniated discs, using techniques like spinal manipulation, traction, and decompression therapy. However, it is important to work with an experienced and knowledgeable chiropractor, as improper treatment can sometimes exacerbate symptoms.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Outlook
Following initial treatment, a rehab protocol focused on strengthening the core and improving flexibility is essential for recovery. Most patients experience significant improvement within three months, and many can return to normal activities after 10 years or more, depending on the severity of the injury and the success of the treatment.
Best Treatment for Herniated Disc
The best treatment for a herniated disc depends on the individual and the severity of their symptoms. For many patients, conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes are effective in managing symptoms. In some cases, alternative treatments like chiropractic care or osteopathic treatment can provide relief. Surgery may be necessary if conservative measures fail or if neurological symptoms worsen. It is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate course of treatment based on individual needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
Herniated discs can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, many patients can achieve long-term relief and return to their normal activities. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals, such as physicians, chiropractors, or osteopaths, to determine the most appropriate course of treatment based on individual needs and circumstances.