Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It can affect various parts of the spine, including the lumbar and thoracolumbar regions. In this blog post, we will explore the intricate aspects of lumbar and thoracolumbar scoliosis, focusing on understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Understanding Different Types of Scoliosis
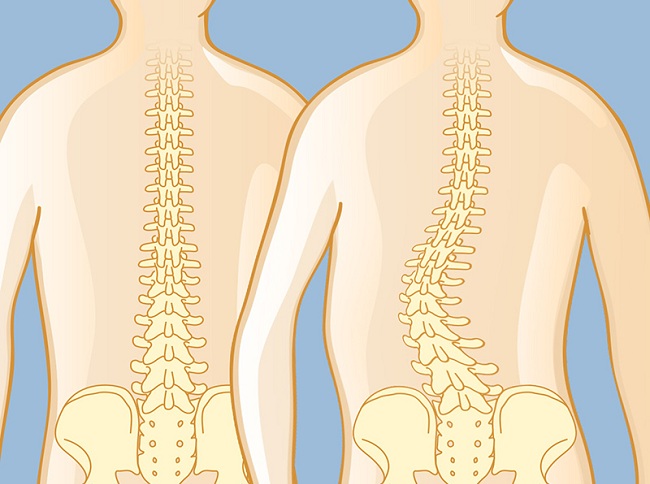
Scoliosis of the Lumbar Spine
Lumbar scoliosis affects the lower portion of the spine, creating an S-shaped or C-shaped curve. It is imperative to monitor this type of scoliosis vigilantly as it can potentially lead to chronic lower back pain and mobility issues.
Right Thoracolumbar Scoliosis
In this variant, the curvature extends from the lower thoracic spine to the upper lumbar spine, veering to the right. It can create imbalance and necessitates careful management to prevent progression.
Lumbar Scoliosis Convex to the Left
This refers to a curve in the lumbar region that bulges outward to the left. It can sometimes be accompanied by a compensatory curve in the opposite direction, a phenomenon that needs a nuanced approach to treatment.
Thoracic and Lumbar Scoliosis
In some cases, scoliosis encompasses both the thoracic (mid-back) and lumbar (lower back) regions, presenting a complex scenario that often requires multifaceted treatment strategies incorporating physical therapy and, in severe cases, surgery.
Diagnostic Codes and Causes
Thoracolumbar Scoliosis ICD 10
In medical parlance, the ICD 10 is a code used to categorize and define various health conditions. Thoracolumbar scoliosis falls under this system, helping healthcare providers to accurately document and treat this specific form of scoliosis.
Thoracolumbar Scoliosis Causes
The exact causes remain largely idiopathic, meaning unknown. However, it can be congenital, arising from vertebral anomalies present at birth, or developed due to neuromuscular conditions, trauma, or infections.
Symptoms and Treatment Modalities
Lumbar Scoliosis Symptoms
Symptoms often encompass chronic pain in the lumbar region, reduced mobility, and visible spinal deformity. Individuals might also experience muscle spasms and nerve symptoms like numbness or tingling in the lower limbs.
Lumbar Scoliosis Treatment
Treatment options include physical therapy, bracing, and in severe cases, surgery. The goal is to manage symptoms effectively and prevent curve progression, fostering better quality of life.
Exercises for Lumbar Scoliosis
Exercise forms a cornerstone of scoliosis management, aiming to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Some beneficial exercises include pelvic tilts, lumbar rotations, and targeted stretching. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of lumbar and thoracolumbar scoliosis facilitates a more tailored approach to management. Whether it is identifying the right exercises or understanding medical terminologies, awareness is your ally in navigating the path to improved spinal health. As always, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice. Stay informed, stay healthy.